Cant Upload to Server Permission Denied Linux
Although SFTP is an easy-to-use and secure file transfer protocol, many people frequently face 1 of the nearly infamous SFTP errors, the "SFTP permission denied."
As the fault output reads, this result is due to the lack of permissions to access a file or directory. By and large, you lot would even so take access to the SFTP server via SSH, but you won't exist able to change a specific file or directory. Another similar error message is the "SFTP permission denied (public key)," where y'all won't even be able to access the server via SFTP or SSH.
In this mail service, we'll go through the two cases. Kickoff, we'll learn to check and update the user/group file/folder permissions, and second, nosotros'll figure out why nosotros are getting authentication/access permission denied due to the public fundamental.
To illustrate a clearer motion picture of the "sftp permission denied" fault scenario, nosotros'll employ an AWS EC2, Ubuntu (Focal-20.04-amd64-server). We will employ the default user "ubuntu" and add a new sftp01 user. Past default, AWS doesn't grant "root" SSH access to the EC2 instances due to security's all-time practices.
1. The "SFTP permission denied" error
Regardless of which SFTP client you use, when you lot SFTP into a server and endeavor to supercede, edit, delete, or overwrite a file or directory, y'all go "an SFTP permission denied" fault bulletin.
An case:
| Cannot create remote file 'ver'. |
| Permission denied. |
| Error code: 3 |
| Mistake message from server: Permission denied |
In Windows, while using an SFTP client, like WinSCP or FileZilla, the message looks like this:
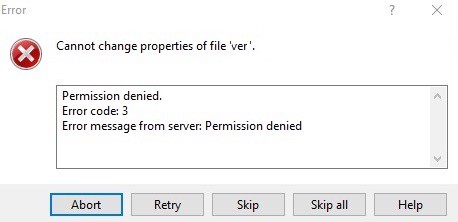
By and large, yous are successfully connecting via SFTP or SSH with the same user, merely yous tin can't modify, change, or overwrite the file via SFTP. Just if y'all cannot even connect via SFTP or SSH, you lot might be getting a similar fault bulletin that reads "SFTP permission denied (public key)".
The reason for these error messages is generally due to incorrect or lack of permissions. For example, you might take read, write, execute permissions on your local file (or folder), but the remote folder (or file) might not be accepting your actions (read, write, or execute).
File permissions 101
Since this fault is most probable related to wrong permissions, you'll have to figure out why you lot don't have the authorization to edit, change, or upload a file or directory.
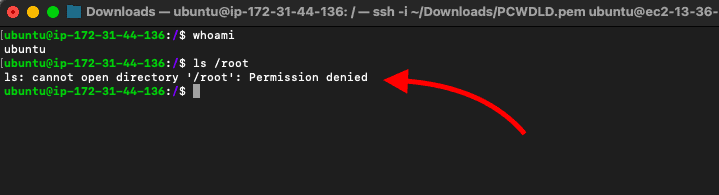
- Log in to the SFTP server using SSH and use the command "$ whoami" to see your username.
- Suppose the user logged in to the SFTP server does not take the necessary permissions (such every bit read command, "ls") to a specific directory or file. In that example, you'll get a bulletin similar: "ls: cannot open up directory '/root': Permission denied".
For security reasons, some cloud providers similar AWS separate root access from other users. In this instance, my "ubuntu" user does not accept admission to the root user's folder. This is simply because both users belong to different groups with unlike permissions.
- Utilize "$ls -l" to become a long detailed list of files, directories, and permissions. This control will help you see whether your user (within a grouping) has the right permissions to a file. The below screenshot shows the output of this command.
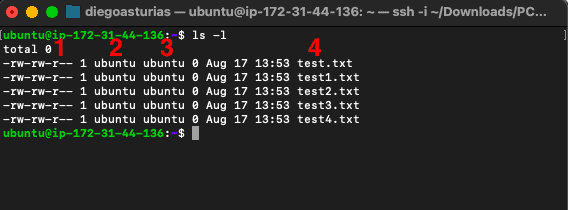
- The relevant output columns:
- (ane)-Permission level The first character, (l or d), represents a symbolic link or directory, while (-) represents a regular file. The next set of three characters (rwx, where: r=read, w=write, x=execute, and – = no permission) stand for user permissions, the side by side 3 stand for group permissions, and the last three characters are "others" permissions.
- (ii, 3)-User and group The adjacent cavalcade (two and 3) represents the file or directory owner and the grouping.
- (four) – Name of the file, directory, or symbolic link.
So, what we tin get from the output is that the file (-) "exam.txt" belongs to the user/group (ubuntu/ubuntu). As for the permission level, "-rw-rw-r—" the "user" and "group" can both read and write, while all others can only read.
- To troubleshoot the SFTP permission denied, you'll need to determine if your "other" user belongs to the group with read and write (rw) permissions (for instance, "ubuntu" in this case).
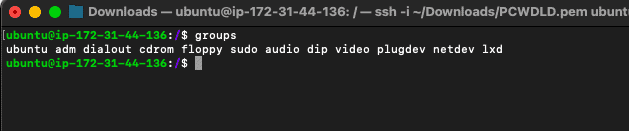
- Use the "$ groups" command to see the grouping your current user is associated with. So, in this case, the user "ubuntu" does non belong to the "root" grouping, and then it does not have access to /root folder, as initially stated. The "sudo" grouping is the one granting elevated privileges.
Solutions: How to fix the SFTP permission denied?
So now that we know how to bank check users, groups, and their file/folder permissions, let'due south solve the "SFTP permission denied" error. Bear in mind that the majority of commands here require higher privilege to execute.
The command (ls -l) is handy to let you lot see the permissions of the target directory or file. If the file or directory belongs to some other user, grouping or information technology does not allow either writing (for case, drwxr-xr-x) for the group and other users, you'll demand to grant the right fix of permissions.
Solution one. Assign the user without permission to a group with permissions to the file or directory
Use the (ls- fifty) command to come across the owner and group a file belongs to. If it belongs to a different group your user does not belong to, you'll demand to assign your user to this group.
Use the post-obit command to assign your user to the grouping permission instead of reading and writing (rw). After doing this, endeavor SFTP once more.
- $ sudo usermod -a -G [target grouping] $USER
Solution 2. Use the (chown) command to modify ownership of the unmarried file or directory
Rather than assign a new group to your user, yous can alter the buying of a file or directory. For example, let's say the "sftp01" user gets an SFTP permission denied every time it wants to edit or overwrite the "test01.txt" file. To see who owns this specific file, go to the binder where you are getting the sftp permission denied and exercise a (ls -l), then utilize (chown) to alter the buying.
- $ sudo chown [user] [file]
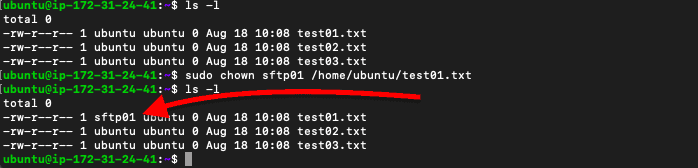
Note: If you are working under an admin or root role, exist careful not to change the unabridged ownership of a directory and subdirectory with -R recursive ownership, every bit this can affect access and authentication to the SFTP server (we'll get to this later).
Solution 3. Grant the appropriate permission
Use the "chmod" command to change the file or directory permissions. The suggested permission levels when using the chmod are 755 for file and 644 for directory permission.
- chmod 755: Read and execute access for anybody. Read, write, and execute access for the owner of the file. For example, when you do a "$chmod 755 examplefile", yous allow everyone to read and perform the file, while only the owner is entitled to read, write, and execute the file.
- chmod 777: Employ the chmod 777 (-rwxrwxrwx) if y'all want to allow anybody, including the owner, grouping, and others, to read, write, and execute. Granting this level of "openness" is non a good security practice, simply you tin employ it for testing purposes.
- chmod 644: The user (or possessor) tin can read, write simply can't execute. The group and others can read but can't write and execute. This command is suggested for directories.
The "$sudo chmod 775 [filename]" command will change the permission construction of the file. As mentioned above, with (-rwxrwxr-10) (775), the file will be readable and executable past everyone (r-x) "others".
![$sudo chmod 775 [filename] command](https://www.pcwdld.com/wp-content/uploads/image2-32.png)
Employ Recursive to add permission subdirectories as well
You lot can use the "sudo chmod -R [mode] [file or directory]". The [-R] changes files and directories recursively, and then use this with care. It allowss the user to read, write, or execute to all sub-directories and files.
Solution four. Permission denied due to failed authentication
Another variation for the SFTP permission denied is due to authentication. You tin't even access your SFTP server from the SFTP client. If you get the "Permission denied (public key)," you won't be able to access and cosign to the server via SSH.
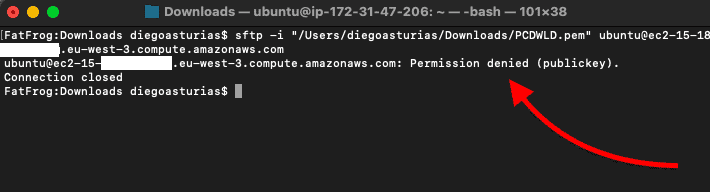
To solve this effect, try the following:
- Check your username Yous might be using the incorrect username, but correct public key and thus get the permission denied mistake. Check whether you are using the correct username in your SFTP client. But still, if the username is correct but is not authorized to use the key, you'll also get permission denied (public central).
- Permissions at the server are incorrect This is because the permission to the files under the home directory changed. Users might be locked out if the "authorized_keys" (under /.ssh/authorized_keys, for Linux Ubuntu) file permission or buying inverse. An admin has to log in with root access or connect via the series console to adjust the dwelling directory file permissions. As mentioned earlier, applying "chmod -R" incorrectly can bear on all home directory subdirectories, including .ssh and authorized_keys files.
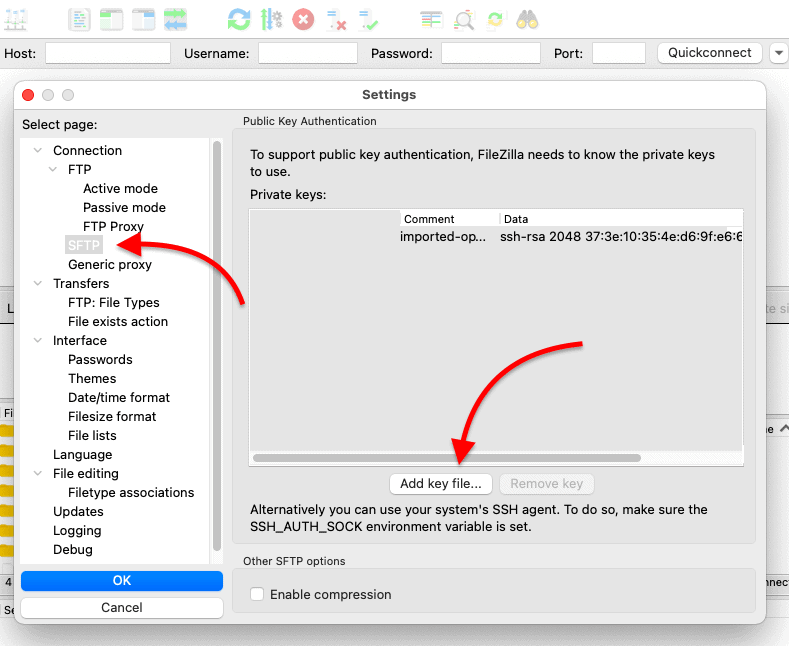
- Check the SSH public central (.pub) on the local computer Make certain you lot are using the right public key in the authorized_keys file. To add together a new public key to an SFTP client with FileZilla. Become to Settings > Connection > SFTP > click on "Add together key file…" Browse through your local files and import the right fundamental.
Configuring permissions with alternative SFTP server tools
1. SolarWinds SFTP/SCP Server – FREE TOOL
The Solarwinds SFTP/SCP server is a free tool for reliable and secure file transfers. It is easy to use, light and runs as a Windows service. In addition, SFTP provides avant-garde SFTP features such as concurrent transfers from multiple devices or limits access by authorizing a specific or range of IPs.
This tool pushes Bone images, configuration files, updates, backup files, or transfer files upwards to 4GB. In improver, this SFTP server provides principal authentication access to the server and only allows i folder for all users.
Website Link: https://www.solarwinds.com/free-tools/gratuitous-sftp-server
Free Download!
2. SolarWinds Serv-U FTP/MFT Server – Free TRIAL
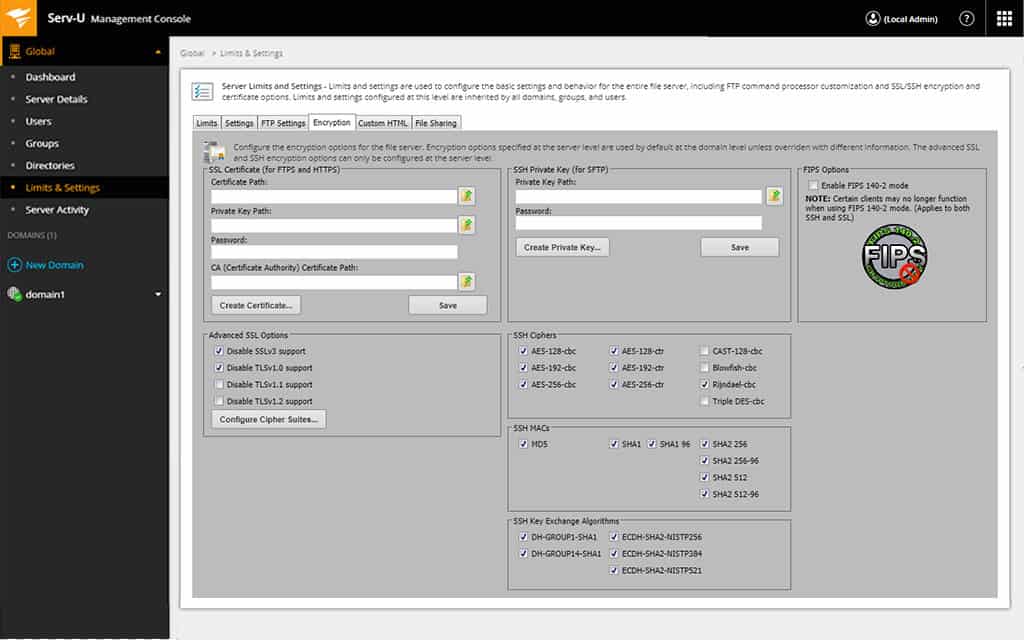
The SolarWinds Serv-U FTP/MFT Server is a more advanced SFTP server that lets you handle big and multiple file transfers. It supports up to 250 users, 100 concurrent sessions, up to 3 domains and allows a fine-grained access control over those resources.
With Serv-U, you lot can easily alter and update user and folder access and permissions. In add-on, it provides a directory admission rule-based control that allows y'all to modify permissions on files and directories.
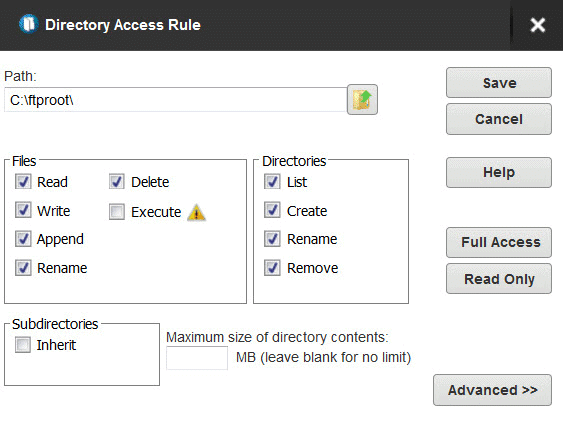
Website Link: https://www.solarwinds.com/serv-u-managed-file-transfer-server
Download 14-day Free Trial!
Final Words
The "SFTP permission denied" error message occurs when your SFTP server doesn't permit your user (within a grouping) to alter or overwrite a file or directory. To solve this, you'll have to SSH into the SFTP server, find the file/directory and identify its current permission mode and ownership. So, you'll have to alter the permissions every bit specified in this mail service. The 2nd SFTP permission denied (public primal) bulletin occurs when y'all are logging with an incorrect user, public key, or the user doesn't have the necessary permission to access the central file in the server.
Alternatively, you can utilise an SFTP server such as SolarWinds Serv-U FTP/MFT Server, which gives y'all more flexibility when configuring permissions. This tool volition help y'all avoid the "SFTP permission denied" and prepare it for all the SFTP users.
Source: https://www.pcwdld.com/troubleshooting-sftp-permission-denied
0 Response to "Cant Upload to Server Permission Denied Linux"
Post a Comment